Carbide laser cladding service
Technical background and process requirements of cemented carbide coatings
Cemented carbide coating technology is a new surface modification technology that emerged with the development of high-power lasers in the 1970s. It refers to the laser surface cladding technology which combines alloy powder or ceramic powder with a laser beam. The surface of the substrate is rapidly heated and melted. After the light beam is removed, the self-excited cooling forms a very low dilution rate. The surface coating is metallurgically combined with the substrate material, thereby significantly improving the wear resistance, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, oxidation resistance and electrical characteristics of the substrate surface. And other surface strengthening methods.
Laser cladding technology has been applied in various fields. Demand is large, including aerospace, rail transportation, metallurgical and petrochemical, engineering machinery, etc. On various kinds of wearing parts such as drilling tools, picks, rolls, ball valves, valve seats and valve stems, after many traditional surface treatment techniques, hard materials are easy to peel off and have a short service life. Laser cladding additive manufacturing technology is now used to completely avoid such problems. Laser cladding technology has been applied to various materials. Laser cladding strengthens the surface of aluminum alloy to increase hardness and wear resistance, opening up the application of aluminum alloy as a moving part of friction pair. Laser cladding technology replaces the hard chromium plating process, which solves the problems of weak bonding strength, easy peeling, and environmental protection of the latter coating and substrate.
Commonly used cemented carbide coating materials: iron-based cemented carbide, cobalt-based wear-resistant alloy, nickel-based superalloy, nickel-based superalloy plus WC ceramic particulate material as reinforcement, and cobalt-based alloy plus WC ceramic particulate material as reinforcement.
Second, the advantages of laser cladding hard alloy
1. The cladding layer has fine grains and dense structure, which can obtain higher hardness, wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
2. During the cladding, a smaller heat affected zone can be generated on the substrate, and the workpiece is less deformed.
3. Metallurgical bonding can be achieved between the cladding layer and the base material, and the dilution rate of the cladding material is low.
4, can be cladding multiple layers, hardness and abrasion resistance are doubled.
5. Selective local fine repair can be achieved, effectively reducing repair costs.
6. The powder material system has high adaptability. Most conventional and special metal powder materials can be cladding on the surface of metal parts.
Performance test results of cemented carbide coating materials
1. Iron-based cemented carbide repair

The metallographic and hardness results after cladding are as follows: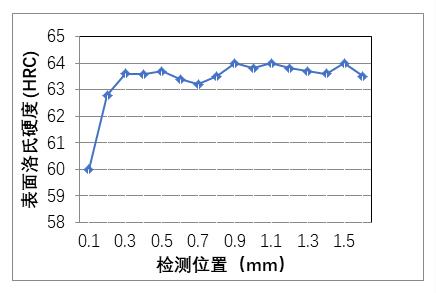
Hardness curve results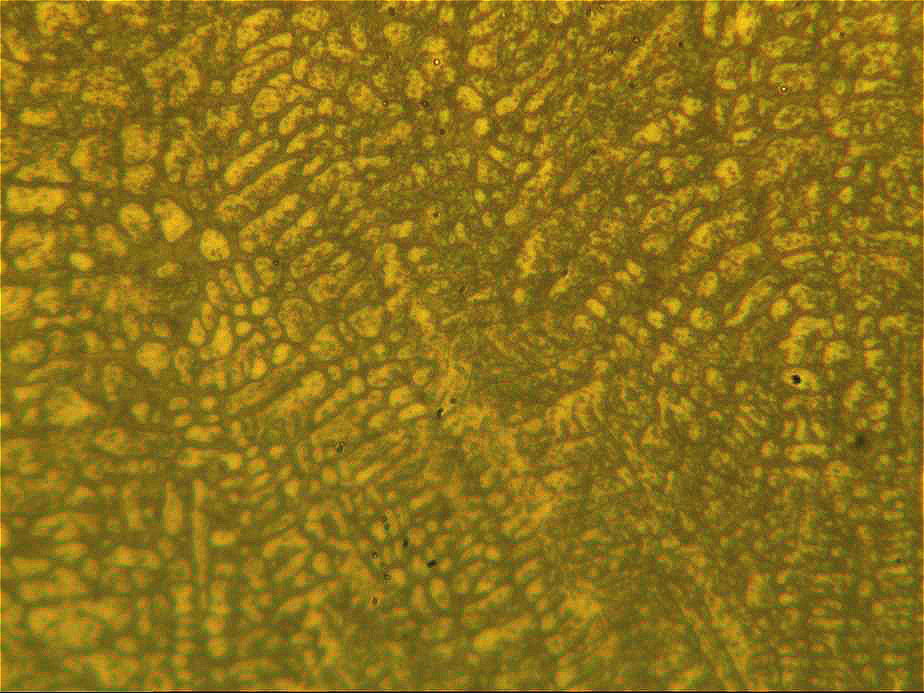
Metallographic structure of 500X cladding layer group
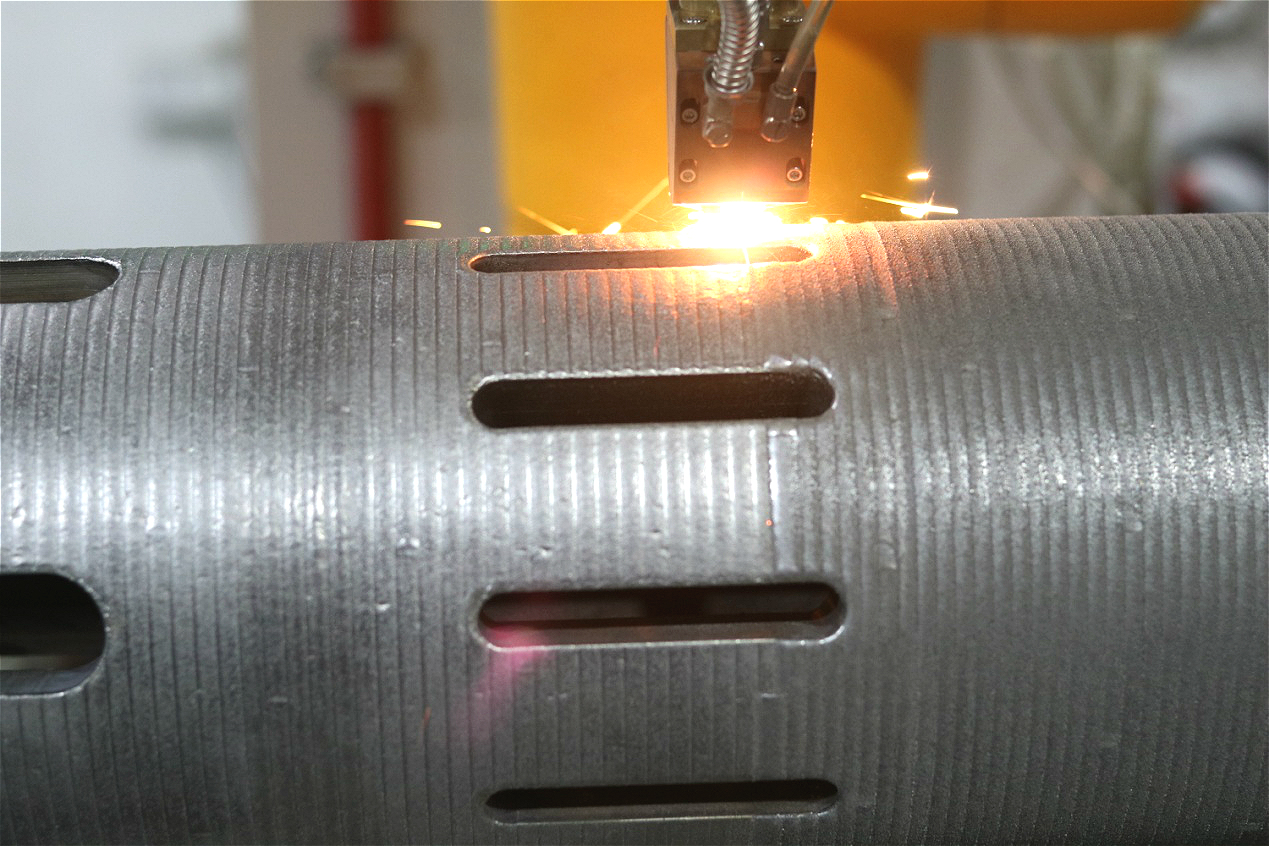
Photo of valve cladding process
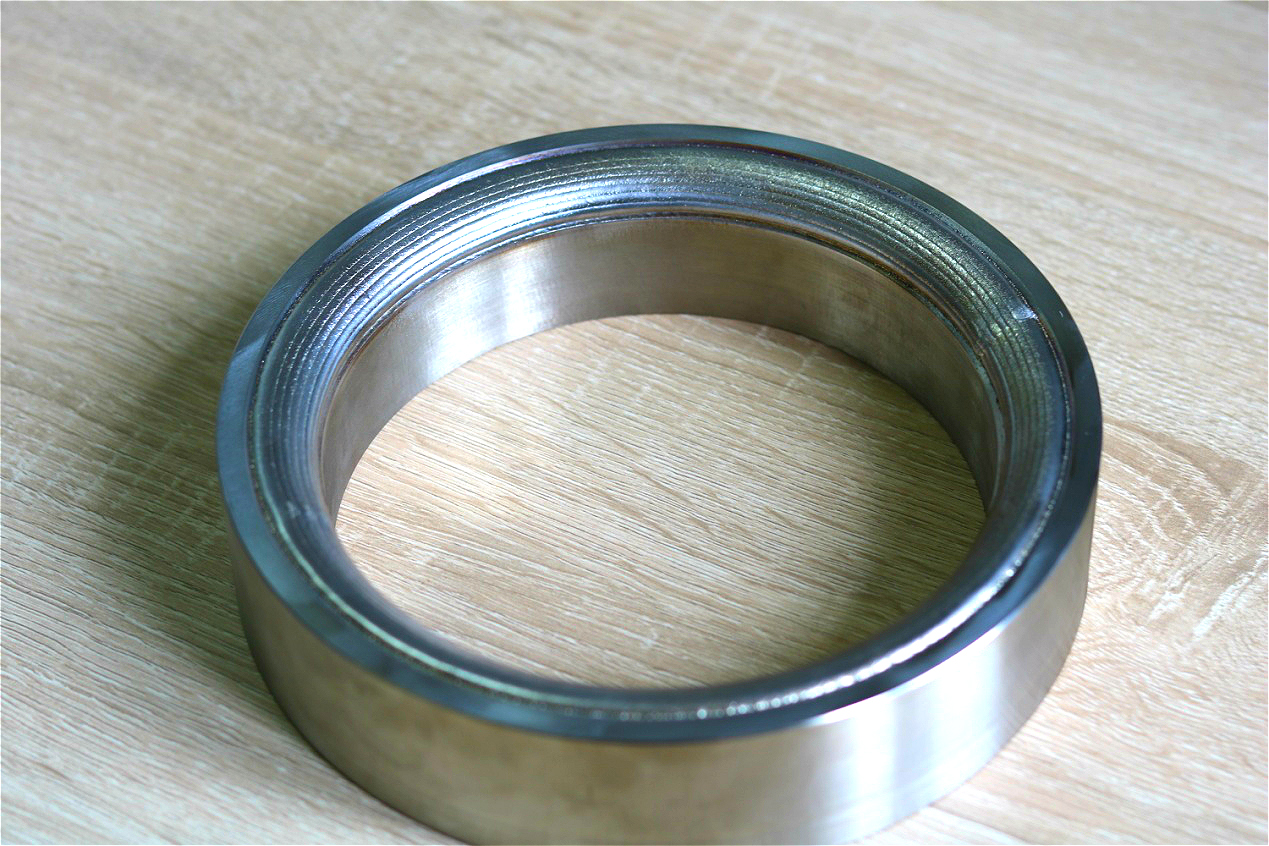
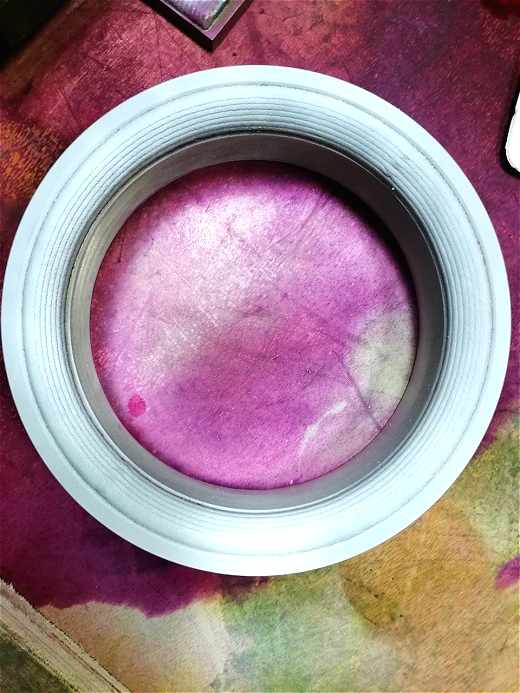


No defect in PT inspection after sealing ring cladding

Serial number | hardness | ||||
Cladding | First group | Second Group | |||
unit | HV0.2 | HRC | HV0.2 | HRC | |
1 | 508.8 | 49.7 | 677.4 | 59.1 | |
2 | 638.6 | 57.3 | 660.3 | 58.3 | |
3 | 643.9 | 57.7 | 671.6 | 58.9 | |
4 | 665.9 | 58.6 | 660.3 | 58.3 | |
5 | 588.7 | 54.7 | 579.5 | 54.2 | |
6 | Substrate | 366.8 | 37.4 | 364.5 | 37.2 |
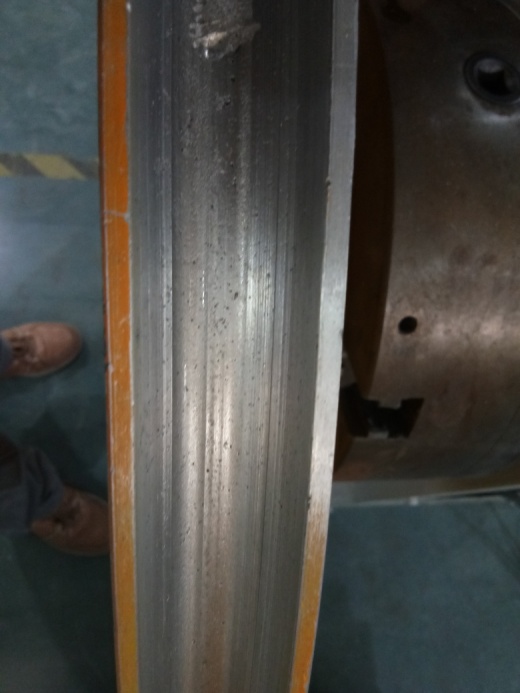

Repair and strengthening of aluminum alloy friction wheel
PT non-destructive testing photos without cracks
Laser cladding additive manufacturing on aluminum alloy surface has good controllability, can cladding multiple layers, and increases hardness and abrasion resistance multiples.
The aluminum alloy is used as the matrix to mix high proportion (volume ratio> 60%) ceramic particles. The metallographic photo is as follows:



Roll sample cladding

The metallographic diagram of a single deposition layer is shown below: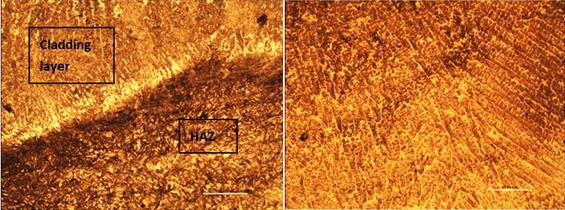
Welding layer 100X Welding layer 500X
The metallographic diagram of multiple overlaps is shown below: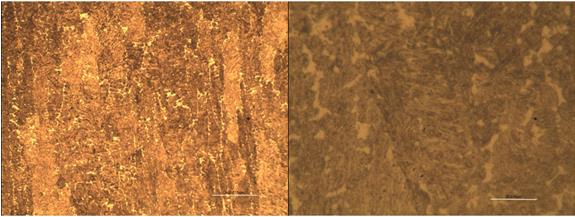
Welding layer 50X Welding layer 100X
Welding layer 200X Welding layer 500X硬度分析:
Rockwell hardness and Vickers microhardness testing were performed on the deposited layer. The data are as follows:
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
Hardness value HRC | 58 | 57 | 58 | 56.5 | 57 |
It can be seen from the hardness value that the hardness distribution is relatively uniform, there is no large hardness inflection point, and the grain distribution is uniform.
4) Pictures of other case parts

Centralizer sleeve repair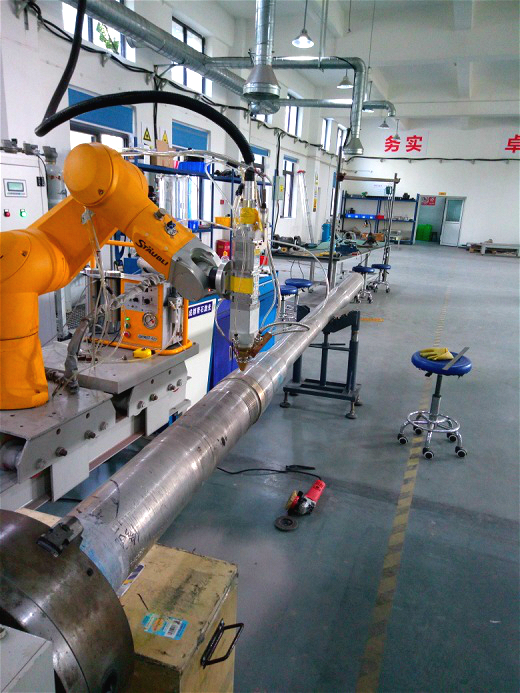
Hardened outer wall of drill tool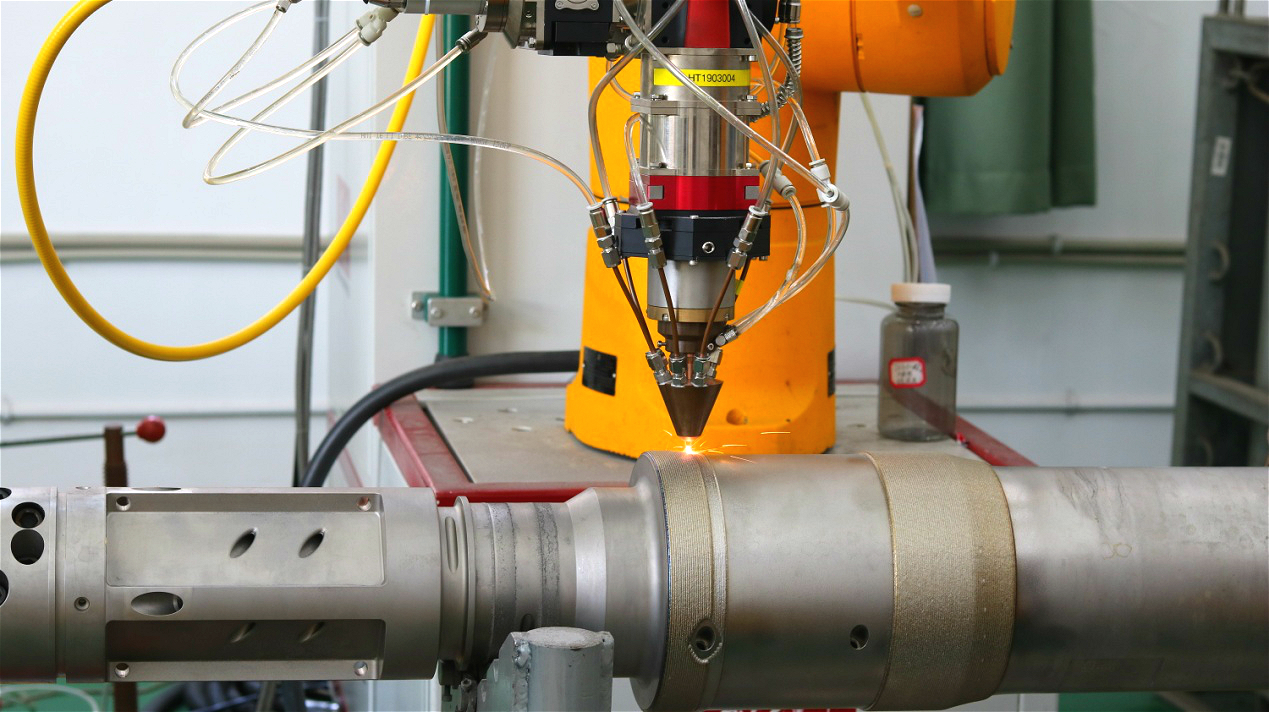
Strengthening of new wear-resistant belts for petroleum drilling tools
